Delicious Foods for Blood Clotting Disorders to Incorporate into Your Diet
Blood clots can be a serious health concern, and lead to conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism or stroke. While medications are often used to prevent or treat blood clots, incorporating certain foods into your diet can help support overall cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of clot formation. You can speak to your doctor about treatment options like Jivi (daamoctocog alfa pegol), a medication that used to help prevent blood clots in people with hemophilia A. This medication is a modified version of factor VIII, which means it helps to replace the missing or low levels of this protein in the body.
Healthy Foods to Eat
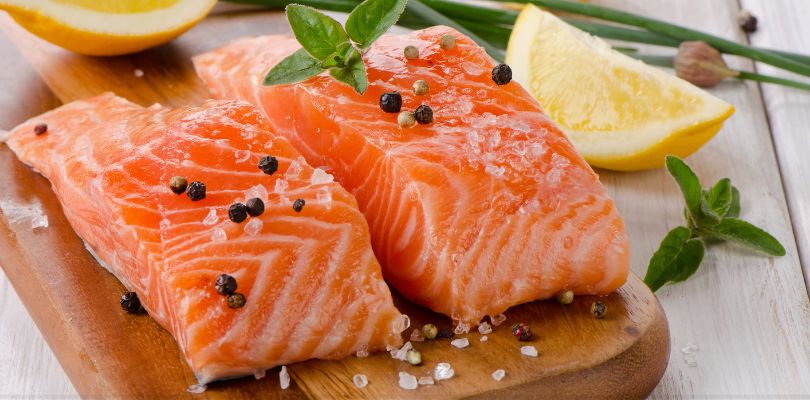
1. Salmon
Salmon, and other fatty fish like mackerel and sardines, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These help reduce inflammation in the body and thin the blood. Omega-3s can prevent excessive clotting by reducing the aggregation of platelets, the blood cells responsible for clot formation. Regular consumption of omega-3-rich fish helps maintain healthy circulation and reduces the risk of clotting disorders.
2. Leafy Greens
Leafy greens like spinach, kale and Swiss chard are high in vitamin K, which plays a crucial role in blood clotting. While vitamin K is often restricted in individuals taking blood thinners like warfarin, it is still essential for those without restrictions, as it helps regulate blood clot formation and prevents excessive clotting. However, it’s important for those with clotting disorders to consult their doctor about vitamin K intake, especially if they are on blood-thinning medications.
3. Garlic
Garlic is known for its natural anticoagulant properties. It contains allicin, a compound that helps thin the blood and prevent the formation of clots. Studies have shown that garlic can reduce platelet aggregation, which helps keep blood flowing smoothly. Incorporating garlic into your diet regularly may help reduce the risk of blood clots.
4. Berries
Blueberries, strawberries and raspberries are high in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, which can help reduce the risk of clot formation. These antioxidants protect blood vessels from damage, improve circulation and reduce inflammation, all of which are factors in preventing blood clots. Berries also promote overall cardiovascular health, which is crucial for individuals with clotting disorders.
This article will explore some treatments for brain tumors, looking at the best options available. Read on to learn more here.
5. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, chia seeds and flaxseeds, are excellent sources of healthy fats, including omega-3s, which help reduce clot formation. In addition to their heart-healthy fats, nuts and seeds are high in fiber, which helps reduce cholesterol levels and improve circulation. Incorporating a handful of nuts or seeds into your daily diet can support cardiovascular health and lower the risk of clots.
6. Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound that has been shown to have blood-thinning properties. Curcumin helps prevent the formation of clots by inhibiting platelet aggregation and reducing inflammation in the blood vessels. Adding turmeric to your meals, whether in soups, stews or smoothies, can be a simple way to help prevent blood clots naturally.
7. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are rich in lycopene, an antioxidant that supports cardiovascular health. Lycopene helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in blood vessels, which can contribute to clot formation. Tomatoes are also a good source of vitamin C, which improves the elasticity of blood vessels and supports overall circulation. Regular consumption of tomatoes may help reduce the risk of blood clotting disorders.
8. Citrus Fruits
Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons and grapefruits are high in vitamin C and flavonoids, both of which are important for maintaining healthy blood vessels and preventing blood clots. Vitamin C helps improve blood vessel function and reduces inflammation, while flavonoids prevent platelet aggregation. Consuming citrus fruits regularly can help support a healthy cardiovascular system and reduce the risk of blood clots.
9. Ginger
Ginger has natural anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant properties that can help prevent blood clots. It contains salicylates, which act similarly to aspirin in preventing clot formation. Ginger also helps improve blood circulation and reduces inflammation in the blood vessels. Drinking ginger tea or adding fresh ginger to your meals can be an easy way to include this clot-preventing food in your diet.
Common Blood Clotting Disorders
Blood clotting disorders can result from either excessive clotting or the inability to clot properly. Here’s a brief overview of some common blood clotting disorders:
1. Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a genetic disorder in which the blood does not clot properly due to the lack of certain clotting factors. People with hemophilia may experience prolonged bleeding after injuries or surgeries. There are two main types: Hemophilia A, caused by a deficiency of factor VIII, and Hemophilia B, caused by a deficiency of factor IX. Treatment often involves clotting factor replacement therapy to prevent and control bleeding episodes.
2. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. This condition can lead to serious complications if the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Risk factors for DVT include prolonged immobility, surgery and certain medical conditions. Treatment includes anticoagulant medications to prevent clot formation and reduce the risk of complications.
3. Von Willebrand Disease
Von Willebrand disease is the most common inherited bleeding disorder, caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of von Willebrand factor, a protein that helps blood platelets stick together to form clots. People with this condition may experience frequent nosebleeds, heavy menstrual periods and prolonged bleeding after surgery or injury. Treatment may include medications to boost von Willebrand factor levels or clotting factor concentrates.
4. Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs, blocking a pulmonary artery. This can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain and coughing up blood. Treatment typically involves blood thinners to dissolve the clot and prevent further clotting.
5. Thrombophilia
Thrombophilia is a condition in which the blood has an increased tendency to form clots. This can be due to genetic factors, such as Factor V Leiden mutation, or acquired conditions, such as antiphospholipid syndrome. People with thrombophilia are at higher risk of developing DVT or pulmonary embolism. Management may include long-term use of blood thinners to prevent clot formation.
Final Notes
Incorporating foods like salmon, leafy greens, garlic and berries into your diet can help support cardiovascular health and prevent blood clots. For individuals with blood clotting disorders, it’s important to work closely with healthcare providers to manage the condition effectively. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, combined with appropriate medical treatments, can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with clotting disorders.